Past Perfect Continuous Tense - Structure, Uses & Examples
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Helping students master long past actions is part of my teaching. This guide breaks it into easy steps with simple explanation and examples.📘 Table of Contents
- 1. Past Perfect Continuous Verb Structure: Had + Been + Verb-ing
- 2. When to Use Past Perfect Continuous Tense?
- 3. Past Perfect Continuous Tense Structure: Basic Sentence Patterns
- 4. Past Perfect Continuous Uses & Examples: Ongoing Past Actions
- 5. 100 Simple Sentences & Classroom Examples
- 6. Practice Time!
- 7. FAQs: Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Let's talk about the past perfect continuous tense! This tense helps us describe actions that were ongoing for a period of time before another action happened in the past. Imagine you're reflecting on what you were doing before a specific moment, like "I had been studying for hours before the exam" or "She had been working hard before she took a break."
Here's how it works: To form the past perfect continuous tense, you use "had been" followed by the base verb with "-ing" added to it. So instead of saying "I study," you say "I had been studying."
Now, why is this helpful? Well, lots of people search for info on grammar, English, or language learning. But sometimes, finding simple explanations can be tough with all the complex stuff out there. That's where we come in!
Understanding the past perfect continuous tense helps you talk about actions or situations that were ongoing and had been going on before something else happened. It's like looking back on what you were up to before a particular moment. Plus, it adds detail and context to your storytelling.
So if you're learning English or just need a refresher, knowing how to use the past perfect continuous tense is pretty cool. And guess what? It's not as hard as it sounds!
1. Past Perfect Continuous Verb Structure: How to Use ‘Had Been + Verb-ing’ Correctly
Verb Structure = had + been + Verb (ing)
In past perfect continuous tense, we use had been + verb-ing. Example: She had been working, They had been studying.
This tense explains a longer action that was happening before another past action.
For example:
- I had been waiting for doctor since 4 O'clock.
- I had been waiting for doctor for two hours.
- Since - Starting point of an action
- For - Duration of an action
2. When to Use Past Perfect Continuous Tense? Learn with Common Examples
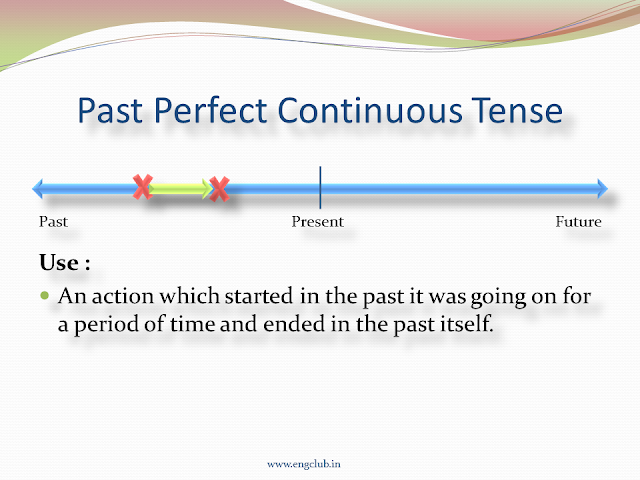
- We use past perfect continuous tense to tell the action which started in the past, it was going on for a period of time and ended in the past itself.
3. Past Perfect Continuous Tense Structure: Easy Grammar Rules for Beginners
3.1 Positive Sentences in Past Perfect Continuous Tense: Learn ‘Had Been + Verb-ing’
Positive : S + had + been + V ing + O.
- I had been playing football since morning.
- You had been practicing English for three months.
- He had been singing since his childhood.
- She had been dancing for 5 years.
- It had been raining for the whole day.
- We had been studying English.
- They had been working in this company since December.
- John had been attending school.
- Birds had been flying in the sky for one hour.
3.2 Negative Sentences in Past Perfect Continuous: Use ‘Had Not Been + Verb-ing’ Easily
Negative : S + had + not + been + V ing + O.
- I had not been playing football since morning.
- You had not been practicing English for three months.
- He had not been singing since his childhood.
- She had not been dancing for 5 years.
- It had not been raining for the whole day.
- We had not been studying English.
- They had not been working in this company since December.
- John had not been attending school.
- Birds had not been flying in the sky for one hour.
3.3 Yes/No Questions in Past Perfect Continuous Tense: Learn to Ask with ‘Had + Subject + Been’
Yes/No type questions: Had + S + been + Verb (ing) + O + ?
- Had you been preparing for exam for two years?
3.4 WH Questions in Past Perfect Continuous Tense: Ask What, Why, Where + Had Been
Wh type questions: Wh word + had + S + been + Verb (ing) + O + ?
- How long had you been preparing for exam?
4. Past Perfect Continuous Tense Uses & Examples: Real-Life Sentences to Master ‘Had Been’
1. Actions That Continued Up to a Point in the Past:
- She had been waiting for the bus for over an hour when it finally arrived.
- They had been playing soccer all afternoon before it started raining.
2. Actions That Had a Duration Before Another Action in the Past:
- By the time we got to the party, she had been dancing for hours.
- He was tired because he had been working all day.
3. Actions That Had Recently Stopped Before Another Past Action:
- When I arrived, she was out of breath because she had been running.
- The room smelled delicious because she had been baking cookies.
4. Emphasizing Duration and Continuity of Past Actions:
- He was exhausted because he had been studying all night.
- She was late because she had been getting ready for hours.
In the past perfect continuous tense, actions that were ongoing for a period of time before another point in the past are described. It's formed by using the past perfect tense of "have" (had been) followed by "been" and the present participle (-ing form) of the main verb.
5. 100 Simple Sentences & Classroom Examples
| Sr. No. | Sentence / Example |
|---|---|
| 1 | The students had been studying for hours before the exam started. |
| 2 | She had been explaining the topic when the principal entered the classroom. |
| 3 | We had been practicing the dialogue before the class presentation. |
| 4 | He had been reading the textbook before the teacher gave instructions. |
| 5 | The teacher had been waiting for the students before starting the lesson. |
| 6 | You had been taking notes when the bell rang. |
| 7 | They had been preparing for the quiz before the announcement was made. |
| 8 | She had been writing her essay for two hours before the deadline. |
| 9 | I had been practicing speaking English before the oral exam. |
| 10 | We had been discussing the project when the teacher asked for updates. |
| 11 | The students had been revising vocabulary before the test. |
| 12 | He had been answering questions before the class ended. |
| 13 | You had been listening carefully before the explanation finished. |
| 14 | She had been studying the new grammar rules before the quiz. |
| 15 | They had been practicing pronunciation before the speech competition. |
| 16 | I had been reading English stories before the reading hour started. |
| 17 | We had been working on group assignments before the break. |
| 18 | The teacher had been correcting papers before the class arrived. |
| 19 | He had been preparing the presentation before the meeting began. |
| 20 | You had been practicing writing before the exam. |
| 21 | She had been explaining the concept for an hour before the students understood. |
| 22 | They had been rehearsing the play before the school festival. |
| 23 | I had been doing my homework before dinner. |
| 24 | We had been discussing the lesson plan before the principal called a meeting. |
| 25 | The students had been chatting before the class started. |
| 26 | He had been working on his science project before the teacher checked progress. |
| 27 | You had been studying English for months before the exam. |
| 28 | She had been listening to the lecture before the power went out. |
| 29 | They had been revising their notes before the final exam. |
| 30 | I had been writing a report before the deadline. |
| 31 | We had been practicing the pronunciation exercises before the test. |
| 32 | The teacher had been preparing the materials before class started. |
| 33 | He had been explaining the rules before the game began. |
| 34 | You had been working hard before the results were announced. |
| 35 | She had been reading aloud before the teacher interrupted. |
| 36 | They had been learning new vocabulary before the quiz. |
| 37 | I had been practicing speaking for an hour before the test. |
| 38 | We had been writing essays before the teacher collected them. |
| 39 | The students had been listening attentively before the question session. |
| 40 | He had been preparing the classroom before the students arrived. |
| 41 | You had been reviewing the lesson before the exam started. |
| 42 | She had been practicing the dialogue before the role-play. |
| 43 | They had been discussing the project details before the meeting. |
| 44 | I had been studying grammar for weeks before the test. |
| 45 | We had been waiting for the teacher before the class began. |
| 46 | The students had been reading silently before the teacher spoke. |
| 47 | He had been explaining the problem before the bell rang. |
| 48 | You had been practicing writing before the assignment was due. |
| 49 | She had been preparing her presentation before the class started. |
| 50 | They had been studying English conversation before the speaking test. |
| 51 | I had been doing my revision before the exam date. |
| 52 | We had been practicing dialogues before the drama class. |
| 53 | The teacher had been organizing the worksheets before the class began. |
| 54 | He had been reading the story before the reading test. |
| 55 | You had been answering questions before the quiz ended. |
| 56 | She had been writing notes before the lecture finished. |
| 57 | They had been rehearsing their speech before the presentation. |
| 58 | I had been working on the assignment before the deadline. |
| 59 | We had been listening to the instructions before the exam. |
| 60 | The students had been studying together before the exam day. |
| 61 | He had been writing his report before the teacher asked for it. |
| 62 | You had been preparing for the test before the holidays. |
| 63 | She had been reading many books before the exam. |
| 64 | They had been practicing the song before the music class. |
| 65 | I had been revising vocabulary before the quiz started. |
| 66 | We had been discussing the answers before the teacher gave feedback. |
| 67 | The teacher had been planning the lesson before the students arrived. |
| 68 | He had been correcting mistakes before the class ended. |
| 69 | You had been working on your project before the deadline. |
| 70 | She had been practicing pronunciation before the speech. |
| 71 | They had been learning new phrases before the oral test. |
| 72 | I had been reading the instructions before starting the test. |
| 73 | We had been revising grammar before the exam. |
| 74 | The students had been discussing answers before the teacher checked. |
| 75 | He had been practicing reading aloud before the class started. |
| 76 | You had been preparing your notes before the presentation. |
| 77 | She had been answering questions before the bell rang. |
| 78 | They had been working on their essays before the deadline. |
| 79 | I had been studying hard before the exams began. |
| 80 | We had been practicing conversations before the speaking test. |
| 81 | The teacher had been preparing the classroom before students arrived. |
| 82 | He had been explaining the topic before the discussion started. |
| 83 | You had been reading the text before answering the questions. |
| 84 | She had been listening to the lecture before taking notes. |
| 85 | They had been revising their lessons before the exam. |
| 86 | I had been writing answers before the time was up. |
| 87 | We had been discussing the topic before the teacher interrupted. |
| 88 | The students had been listening quietly before the bell rang. |
| 89 | He had been preparing for the test before the holidays started. |
| 90 | You had been practicing your speech before the presentation. |
| 91 | She had been working on the project before the deadline. |
| 92 | They had been revising vocabulary before the quiz. |
| 93 | I had been reading for hours before the test. |
| 94 | We had been practicing grammar exercises before the exam. |
| 95 | The teacher had been explaining the lesson before the break. |
| 96 | He had been answering questions before the quiz ended. |
| 97 | You had been reading aloud before the teacher stopped you. |
| 98 | She had been practicing writing before the assignment was due. |
| 99 | They had been learning new words before the test. |
| 100 | I had been listening to English songs before the class started. |
6. Practice Time!
- I _______ (study) for hours before the test started.
- They _______ (work) on the project when I joined the team.
- She _______ (not feel) well for days before she went to the doctor.
- Had you _______ (exercise) regularly before the injury?
- He _______ (read) the book for a month before he finished it.
- had been studying
- had been working
- had not (hadn’t) been feeling
- been exercising
- had been reading
English Tenses Comparison Table
| Tense | Usage | Structure | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Present Tense | Daily routines, facts | Subject + base verb / verb+s | She reads every day. |
| Present Continuous Tense | Actions happening now | Subject + is/am/are + verb+ing | I am studying English. |
| Present Perfect Tense | Recently completed actions | Subject + has/have + past participle | They have finished homework. |
| Present Perfect Continuous Tense | From past to now | Subject + has/have been + verb+ing | He has been working since morning. |
| Simple Past Tense | Completed actions in the past | Subject + past verb | We visited the zoo yesterday. |
| Past Continuous Tense | Specific time past actions | Subject + was/were + verb+ing | She was cooking at 8 PM. |
| Past Perfect Tense | Before another past action | Subject + had + past participle | They had left before I arrived. |
| Past Perfect Continuous Tense | Ongoing past action | Subject + had been + verb+ing | I had been reading for two hours. |
| Simple Future Tense | Future facts or decisions | Subject + will + base verb | She will call you tomorrow. |
| Future Continuous Tense | Action in progress in future | Subject + will be + verb+ing | I will be sleeping at 11 PM. |
| Future Perfect Tense | Done before a future time | Subject + will have + past participle | We will have arrived by noon. |
| Future Perfect Continuous Tense | Ongoing till future time | Subject + will have been + verb+ing | She will have been working for 5 years. |
📘 Learn All 12 English Tenses
7. FAQs: Past Perfect Continuous Tense
1. What is the Past Perfect Continuous Tense?
2. When do we use it?
3. How do we form it?
4. Common mistakes?
5. Questions and negatives?
References
- Murphy R. (2019). English grammar in use: A self-study reference and practice book for intermediate learners of English (5th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
- Purdue University Online Writing Lab. (n.d.). Verb tense consistency. https://owl.purdue.edu
- BBC Learning English. (n.d.). Grammar lessons: Past perfect continuous tense. https://www.bbc.co.uk/learningenglish
- Dave’s ESL Cafe. (n.d.). Grammar lessons for English learners. https://www.eslcafe.com
- Quirk R., Greenbaum S., Leech G. & Svartvik J. (1985). A comprehensive grammar of the English language. Longman.
- Azar B. S. (2009). Understanding and using English grammar (4th ed.). Pearson Education.
- Swan M. (2005). Practical English usage (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press.
- Eastwood J. (1994). Oxford guide to English grammar. Oxford University Press.
- Thomson A. & Martinet A. V. (1986). A practical English grammar (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
- Celce-Murcia M., & Larsen-Freeman D. (1999). The grammar book: An ESL/EFL teacher's course (2nd ed.). Heinle & Heinle Publishers.
- Seely J. (2004). Oxford English grammar course: Basic. Oxford University Press.
- Nunan D. (2003). Practical English language teaching (2nd ed.). McGraw-Hill.
- Richards J. C., & Schmidt R. (2010). Longman dictionary of language teaching and applied linguistics (4th ed.). Pearson Education.
- Lewis M. (1993). The English verb: An exploration of structure and meaning (2nd ed.). Collins ELT.
- Hewings M. (2005). Advanced grammar in use (2nd ed.). Cambridge University Press.
- Biber D., Conrad S., & Leech G. (2002). Longman grammar of spoken and written English. Pearson Education.
- Carter R., & McCarthy M. (2006). Cambridge grammar of English: A comprehensive guide to spoken and written grammar and usage. Cambridge University Press.